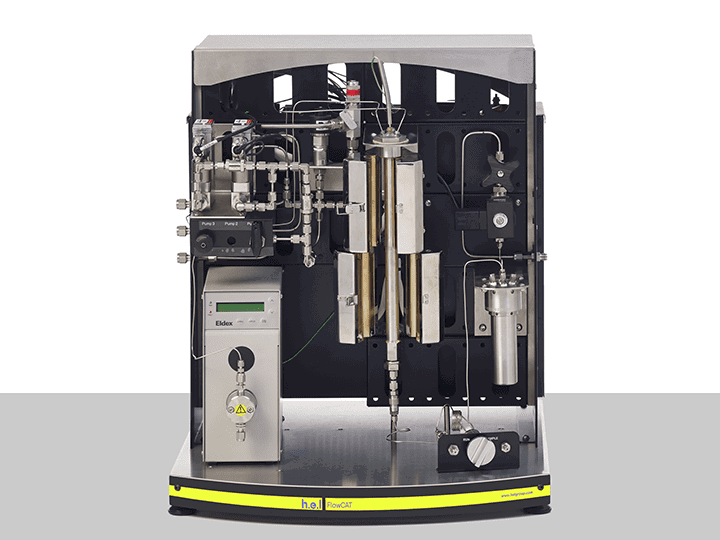
FlowCAT | A Bench-Top, High Pressure Flow Catalysis Platform
The FlowCAT is an automated high-pressure flow catalysis bench-top platform, designed for the development of continuous flow chemical processes. It supports both gas and liquid feeds, and so can facilitate the scale-up of both homogenous and heterogenous chemistries. It typically finds use in chemistries such as:
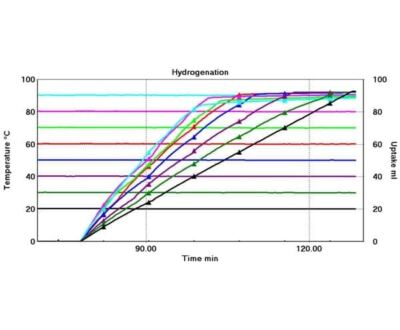
- Hydrogenation
- Oxidation
- Carbonylation
- Bio-fuel research
- Fischer-Tropsch synthesis
- Petrochemical processes
Control of the chemical process is configurable, and it can be tailored to automatically cover a range of process conditions – the latter of which can also be edited during operation if required. The temperature, pressure, and feed rates of the liquid and gas are all automatically controlled, as is the sampling at the end of each run and the initiation of the next. This delivers a high throughput operation, making the FlowCAT well-suited to a range of applications, including:
- Rapid screening of new chemistries
- Yield optimization studies
- Identification of new catalysts
- Small-scale production
Application Notes:
- Investigating Zinc Oxide-Modified Mordenite as an Effective Catalyst for the Dehydrogenation of Ethanol utilizing the FlowCAT
- In this study, the H.E.L FlowCAT was used for the development and optimization of a process for the production of acetaldehyde via the dehydrogenation of bioethanol. This is the first stage toward a multistep reaction, taking ethanol to higher-value chemicals. This work was carried out at Durham University by Dr. Russell Taylor and Samuel Raynes, to whom all work is accredited. A full copy of the paper is available from the RSC.
- Investigating a Sponge Metal Catalysts in a Trickle Bed Reactor for Continuous Hydrogenation Inflow
- In this study, the H.E.L. FlowCAT was used to optimize inflow the reductive hydrogenation of an aliphatic nitro intermediate using a sponge nickel catalyst in a trickle bed reactor. Once optimal conditions were established, 1.2 kg of reagent was successfully reduced via the FlowCAT, with a yield of approximately 90% over a period of 19 hours. This work was carried out by the Chemical Development team and the Clinical Supply Chain team at GSK, to whom all work is accredited.
On-Demand Webinars:
- Flow Chemistry Mini-Symposium 2021: discussing the benefits and challenges of transferring batch into flow process
- Presentations from flow and catalysis experts, discussing the benefits and challenges of transferring batch into flow process. Following the presentations, the presenters answer questions from the audience.
- Evaluation of Catalysts in a Trickle Bed Reactor for Continuous Hydrogenations (Lee Edwards | GSK)
- Cascade Conversion of Biomass Platform Chemicals with Multifunctional Zeolitic Materials (Sam Raynes & Russell Taylor | Durham University)
- Taming High Energy Photochemical Processes with Flow: Case Studies and Future Perspectives (Joshua-Philip Barham | University of Regensburg)
- Presentations from flow and catalysis experts, discussing the benefits and challenges of transferring batch into flow process. Following the presentations, the presenters answer questions from the audience.
Blogs:
- Beginner’s Guide to Flow Chemistry
- For many, a journey into flow chemistry has just begun; therefore, understanding the key aspects of this process is extremely important. Flow chemistry can provide excellent solutions to the chemical industry when utilizing the best and most appropriate technologies to meet demands.
- Exploring the pitfalls of Flow Chemistry – industry and academic insight
- Recently, H.E.L invited four specialist flow chemistry practitioners to speak at an online symposium on the topic. After the speakers had shared their research and experiences and answered questions from delegates, we took the opportunity to ask some questions of our own. Here, our speakers share their own 'pain points' of working in flow.
- Batch Versus Flow in Pharma: The upsides of continuous chemistry
- Does today's take-up of flow chemistry in fields such as photochemistry, electrochemistry, and hazardous gas usage mean that the days are numbered for parallel batch reactor testing? We've been talking to leading experts in flow catalysis in pharmaceutical companies to determine how they address this topic.
Technical Literature
The following is a list of supporting Technical Literature.
Investigating Zinc Oxide-Modified Mordenite as an Effective Catalyst for the Dehydrogenation of Ethanol utilizing the FlowCAT
Investigating a Sponge Metal Catalysts in a Trickle Bed Reactor for Continuous Hydrogenation Inflow
Publications
The following are a list of some technical publications which highlight the use of the equipment.
Evaluation and Screening of Spherical Pd/C for Use as a Catalyst in Pharmaceutical-Scale Continuous Hydrogenations
Eneritz Fernandez-Puertas, Andrew J. Robinson, Hannah Robinson, Shainthavaan Sathiyalingam, Heather Stubbs, and Lee J. Edwards
01-Jun-2020
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.oprd.0c00183(Subscription or purchase maybe required for full access)
Continuous Flow Synthesis. A Pharma Perspective
Laia Malet-Sanz and Flavien Susanne
01-Jan-2020
https://doi.org/10.1021/jm2006029(Subscription or purchase maybe required for full access)
Evaluation of Sponge Metal Catalysts in a Trickle Bed Reactor for the Continuous Hydrogenation of an Aliphatic Nitro Intermediate
Antonella Carangio, Lee J. Edwards, Eneritz Fernandez-Puertas, Jerome F. Hayes, Maciej M. Kucharski, Graham W. Rutherford, Katherine M. P. Wheelhouse, and Glynn D. Williams
01-Jan-2020
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.oprd.9b00447(Subscription or purchase maybe required for full access)
Flow fine synthesis with heterogeneous catalyst
Koichiro Masuda, Tomohiro Ichitsuka, Nagatoshi Koumura, Kazuhiko Sato, Shū Kobayashi
01-Apr-2018
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2018.02.006 (Subscription or purchase maybe required for full access)
High-yielding continuous-flow synthesis of antimalarial drug hydroxychloroquine
Eric Yu‡ORCID Logo, Hari P. R. Mangunuru‡ORCID Logo, Nakul S. TelangORCID Logo, Caleb J. Kong, Jenson Verghese, Stanley E. Gilliland IIIORCID Logo, Saeed Ahmad, Raymond N. Dominey and B. Frank Gupton
01-Mar-2018
https://doi.org/10.3762/bjoc.14.45(Subscription or purchase maybe required for full access)
Solvent-Free Continuous Operations Using Small Footprint Reactors: A Key Approach for Process Intensification
https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b00287
01-Mar-2016
https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b00287(Subscription or purchase maybe required for full access)
Process Intensification for the Continuous Flow Hydrogenation of Ethyl Nicotinate
Takashi Ouchi,†,‡ Claudio Battilocchio,† Joel M. Hawkins,§ and Steven V. Ley
01-Jul-2014
https://doi.org/10.1021/op500208j(Subscription or purchase maybe required for full access)
Adsorption of dimethyl ether (DME) on zeolite molecular sieves
Jai B.LadYassir T.Makkawi
01-Jul-2014
http://publications.aston.ac.uk/id/eprint/23396/1/Adsorption_of_dimethyl_ether_DME_on_zeolite_molecular_sieves.pdf (Subscription or purchase maybe required for full access)
The H.E.L FlowCAT is a very robust, compact and flexible apparatus for high pressure heterogeneous catalytic processes. Its small footprint and versatility, along with the advantage of having reliable safety features, make the H.E.L FlowCAT an excellent piece of equipment to use. It has impressive potential for scaling up procedures.

Cranfield University is working with H.E.L group on the design and manufacture of custom automated synthesisers for production of artificial ”Plastic Antibodies”. By combining the expertise from Cranfield University on the synthetic process with automation and custom fabrication know-how of H.E.L, a range of synthesisers were produced, including a new near-production prototype. Our experience with the new automated reactor/synthesiser showed that it can perform reproducible synthetic cycles under controlled conditions and with minimal operator input.

Currently Teva is using H.E.L CAT 7 hydrogenation system. It was effectively used for screening of hydrogenation catalysts and determination of optimal hydrogenation conditions. Our experience with CAT 7 system showed that it can significantly reduce the time needed for a selection of hydrogenation conditions, mostly by rapid identification of the most relevant screening hits for the further research and development process. In conclusion, H.E.L CAT 7 was found to be very useful choice for our R&D.
Teva Czech Industries - Teva Czech Industries