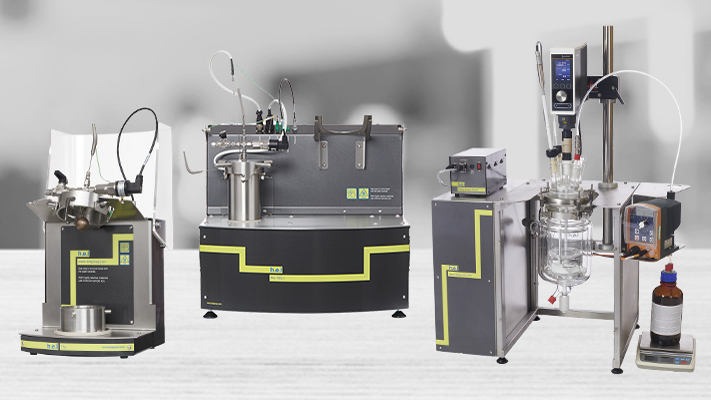
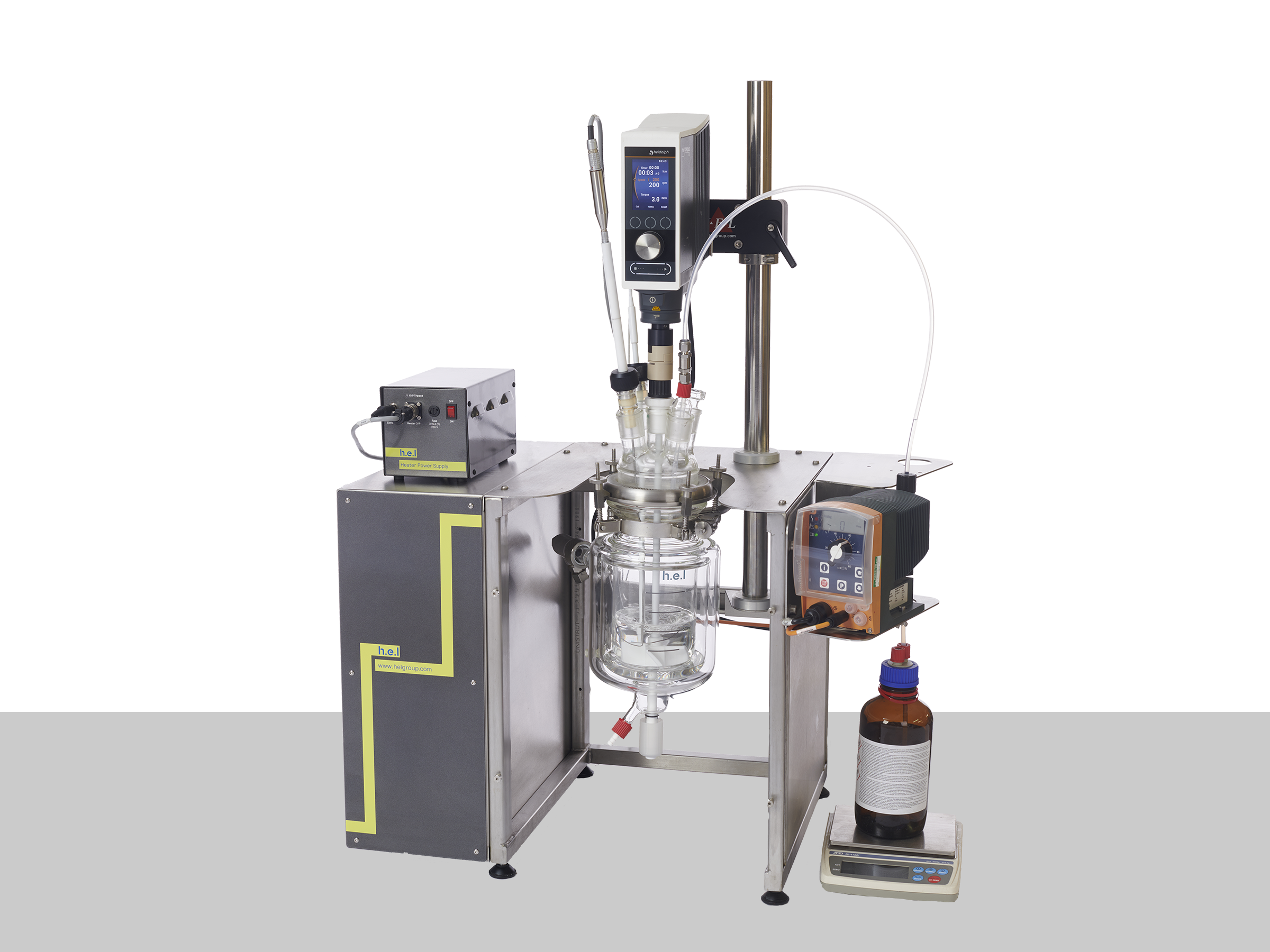
Meet Global Safety Standards
Our process safety systems align with key international regulations to help you evaluate chemical hazards, stay compliant, and scale up safely.
Supported Standards
Key Safety Parameters Measured
| Adiabatic Calorimetry | Isothermal Calorimetry |
|---|---|
|
|
Why Process Safety Matters
Uncontrolled reactions can lead to rapid temperature and pressure spikes, causing thermal runaway, explosions, or toxic releases. Identifying and mitigating these risks is essential to ensuring safety, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency
Process safety workflow
Discovery – Chemical Reaction Route Selection & Thermal Screening
Thermal screening helps identify the safest and most efficient route for synthesizing your target molecule. By evaluating safety, complexity, and cost, we ensure that decisions made early in the process minimize risks.
Key Parameters to Obtain During Thermal Screening:
- Onset temperature of decomposition (Td)
- Rate of temperature increase (dT/dt and d²T/dt²)
- Rate of pressure increase (dP/dt)
Process Development and Optimization
At this stage, the focus is on optimizing chemical routes to improve yield, quality, and safety while reducing hazards. Safety is integrated early to establish a strong foundation for small-scale production.
Key safety factors include:
- Reactant accumulation & heat evolution
- Heat capacity & adiabatic temperature rise
- Maximum Temperature of Synthesis Reaction (MTSR)
- Cooling requirements
Safe handling and storage of materials
A key aspect of process development is also ensuring the safe handling and storage of materials. Thermally unstable substances can react at certain temperatures, leading to risks like decomposition, pressure buildup, or explosions. Evaluating thermal stability helps define safe storage conditions and minimize hazards.
Process Scale-Up & Hazard Mitigation
Scaling up a chemical process requires understanding potential hazards. A Process Hazard Analysis (PHA) identifies risks and anticipates worst-case scenarios to ensure safe operations. Key methods include HAZOP, FMEA, Fault Tree Analysis, and Batch Sheet Review.
Adiabatic calorimetry (Phi-TEC I & II) simulates worst-case thermal scenarios, ensuring accurate heat retention and industrial conditions.
Key insights from testing include:
- Tempering Characteristics – Can vapors control heat?
- Discharge Nature – Will the reaction release gas only or a liquid-gas mix?
- These insights are essential for accurate vent sizing and relief system design.
Process safety workflow
Discovery – Chemical Reaction Route Selection & Thermal Screening
Thermal screening helps identify the safest and most efficient route for synthesizing your target molecule. By evaluating safety, complexity, and cost, we ensure that decisions made early in the process minimize risks.
Key Parameters to Obtain During Thermal Screening:
- Onset temperature of decomposition (Td)
- Rate of temperature increase (dT/dt and d²T/dt²)
- Rate of pressure increase (dP/dt)
What our Customers Say

My experience with H.E.L dates since 2005. During these years H.E.L was the provider of the most important lab equipment with the help of which I developed many different API pharmaceutical processes in the companies l worked for including Merck, Pfizer, and Theravance. The versatility of the automated lab reactors (AutoLAB), the ease of use of and the accuracy of the TSu and Simular systems, as well as the flexibility of the PolyBLOCK made my work much easier and accurate. I would like to mention the great relationship I established with the service engineers and the sales people at H.E.L. With their help I was able to customize the software and the hardware of the equipment to our specific needs. This readiness to accommodate each customer’s specific needs gives H.E.L the edge over their competitors and makes them the preferred vendor for pharmaceutical lab equipment.
Process Development and Optimization
At this stage, the focus is on optimizing chemical routes to improve yield, quality, and safety while reducing hazards. Safety is integrated early to establish a strong foundation for small-scale production.
Key safety factors include:
- Reactant accumulation & heat evolution
- Heat capacity & adiabatic temperature rise
- Maximum Temperature of Synthesis Reaction (MTSR)
- Cooling requirements
Safe handling and storage of materials
A key aspect of process development is also ensuring the safe handling and storage of materials. Thermally unstable substances can react at certain temperatures, leading to risks like decomposition, pressure buildup, or explosions. Evaluating thermal stability helps define safe storage conditions and minimize hazards.
What our Customers Say

My experience with H.E.L dates since 2005. During these years H.E.L was the provider of the most important lab equipment with the help of which I developed many different API pharmaceutical processes in the companies l worked for including Merck, Pfizer, and Theravance. The versatility of the automated lab reactors (AutoLAB), the ease of use of and the accuracy of the TSu and Simular systems, as well as the flexibility of the PolyBLOCK made my work much easier and accurate. I would like to mention the great relationship I established with the service engineers and the sales people at H.E.L. With their help I was able to customize the software and the hardware of the equipment to our specific needs. This readiness to accommodate each customer’s specific needs gives H.E.L the edge over their competitors and makes them the preferred vendor for pharmaceutical lab equipment.
Process Scale-Up & Hazard Mitigation
Scaling up a chemical process requires understanding potential hazards. A Process Hazard Analysis (PHA) identifies risks and anticipates worst-case scenarios to ensure safe operations. Key methods include HAZOP, FMEA, Fault Tree Analysis, and Batch Sheet Review.
Adiabatic calorimetry (Phi-TEC I & II) simulates worst-case thermal scenarios, ensuring accurate heat retention and industrial conditions.
Key insights from testing include:
- Tempering Characteristics – Can vapors control heat?
- Discharge Nature – Will the reaction release gas only or a liquid-gas mix?
- These insights are essential for accurate vent sizing and relief system design.
What our Customers Say
No Testimonials found.
Discovery – Chemical Reaction Route Selection & Thermal Screening
Thermal screening helps identify the safest and most efficient route for synthesizing your target molecule. By evaluating safety, complexity, and cost, we ensure that decisions made early in the process minimize risks.
Key Parameters to Obtain During Thermal Screening:
- Onset temperature of decomposition (Td)
- Rate of temperature increase (dT/dt and d²T/dt²)
- Rate of pressure increase (dP/dt)
Process Development and Optimization
At this stage, the focus is on optimizing chemical routes to improve yield, quality, and safety while reducing hazards. Safety is integrated early to establish a strong foundation for small-scale production.
Key safety factors include:
- Reactant accumulation & heat evolution
- Heat capacity & adiabatic temperature rise
- Maximum Temperature of Synthesis Reaction (MTSR)
- Cooling requirements
Safe handling and storage of materials
A key aspect of process development is also ensuring the safe handling and storage of materials. Thermally unstable substances can react at certain temperatures, leading to risks like decomposition, pressure buildup, or explosions. Evaluating thermal stability helps define safe storage conditions and minimize hazards.
Process Scale-Up & Hazard Mitigation
Scaling up a chemical process requires understanding potential hazards. A Process Hazard Analysis (PHA) identifies risks and anticipates worst-case scenarios to ensure safe operations. Key methods include HAZOP, FMEA, Fault Tree Analysis, and Batch Sheet Review.
Adiabatic calorimetry (Phi-TEC I & II) simulates worst-case thermal scenarios, ensuring accurate heat retention and industrial conditions.
Key insights from testing include:
- Tempering Characteristics – Can vapors control heat?
- Discharge Nature – Will the reaction release gas only or a liquid-gas mix?
- These insights are essential for accurate vent sizing and relief system design.
Case Study: Decomposition of di-tert-butyl peroxide
Objective
To determine the onset temperature for the decomposition of di-tert-butyl peroxide (DTBP).
Requirement
Identify the onset temperature and potential pressure-link risks of the decomposition reaction of DTBP
Solution
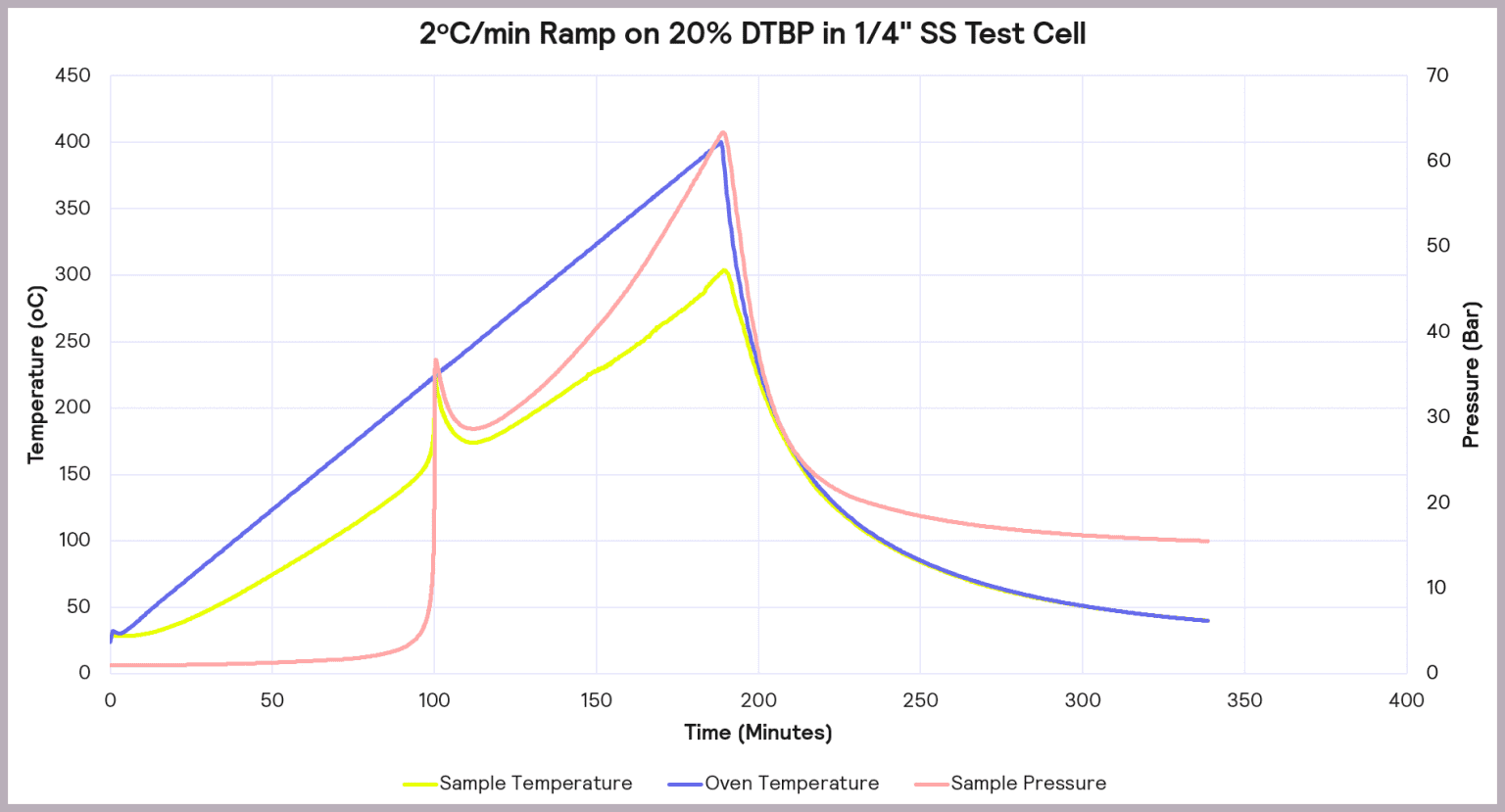
To understand the stability of DTBP a TSu was used. It allowed to heat up the oven at a rate of 2ºC·min-1 and track the oven and sample temperature and well as pressure. When the sample starts to decompose, its temperature and pressure increase faster than the oven’s, showing that a reaction is occurring
Results
The thermal behavior of a 20% DTBP solution in toluene was performed. Around the 100 min mark there is a sudden increase in both temperature and pressure, indicating the beginning of a decomposition reaction at around 45ºC. At this point the temperature reached 225ºC and 43 bar of pressure.
What our Customers Say

My experience with H.E.L dates since 2005. During these years H.E.L was the provider of the most important lab equipment with the help of which I developed many different API pharmaceutical processes in the companies l worked for including Merck, Pfizer, and Theravance. The versatility of the automated lab reactors (AutoLAB), the ease of use of and the accuracy of the TSu and Simular systems, as well as the flexibility of the PolyBLOCK made my work much easier and accurate. I would like to mention the great relationship I established with the service engineers and the sales people at H.E.L. With their help I was able to customize the software and the hardware of the equipment to our specific needs. This readiness to accommodate each customer’s specific needs gives H.E.L the edge over their competitors and makes them the preferred vendor for pharmaceutical lab equipment.
Case Study: Thermal Hazards in the Synthesis of a Grignard Reagent
Objective
To evaluate the thermal hazards associated with synthesizing a Grignard reagent under different dosing rates.
Requirement
Assess the effect of dosing rate on thermal accumulation and runaway reaction risk. Identify the most hazardous phase in the process to improve safety measures.
Solution
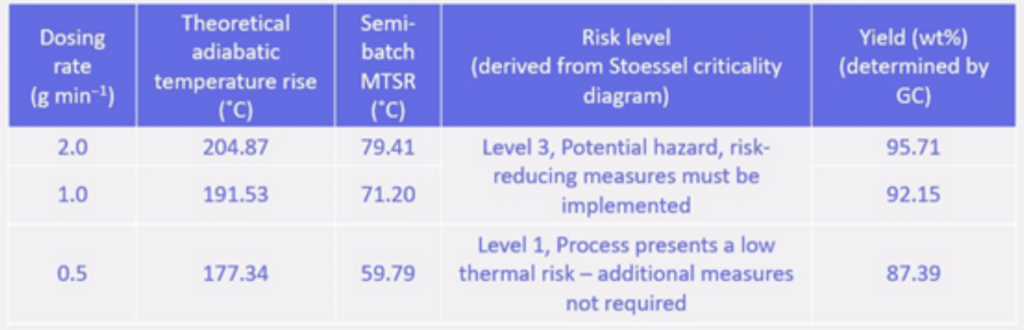
A reaction calorimeter (SIMULAR) was used to analyze the heat release during Grignard reagent synthesis at different dosing rates (0.5–2.0 g·min⁻¹). Results showed that lower dosing rates significantly reduced heat accumulation and overall reaction risk.
Results
The synthesis process exhibited a high heat release, with total reaction enthalpies ranging from 362.69 to 397.11 kJ·mol⁻¹. A lower dosing rate (0.5 g·min⁻¹) minimized thermal accumulation, reducing the risk of thermal runaway. The most hazardous phase was the induction period, where heat buildup was highest.
Conclusion
The study demonstrated that dosing rate is a critical parameter in managing the thermal hazards of Grignard reagent synthesis. A lower dosing rate significantly reduces heat accumulation and mitigates the risk of runaway reactions, making the process safer. Additionally, while the Grignard reagent remains stable under normal conditions, careful control of the induction phase is essential to prevent hazardous thermal accumulation. These findings provide valuable insights for safer scale-up and industrial applications.
What our Customers Say

My experience with H.E.L dates since 2005. During these years H.E.L was the provider of the most important lab equipment with the help of which I developed many different API pharmaceutical processes in the companies l worked for including Merck, Pfizer, and Theravance. The versatility of the automated lab reactors (AutoLAB), the ease of use of and the accuracy of the TSu and Simular systems, as well as the flexibility of the PolyBLOCK made my work much easier and accurate. I would like to mention the great relationship I established with the service engineers and the sales people at H.E.L. With their help I was able to customize the software and the hardware of the equipment to our specific needs. This readiness to accommodate each customer’s specific needs gives H.E.L the edge over their competitors and makes them the preferred vendor for pharmaceutical lab equipment.
Case Study: Vent Sizing for Runaway Reactions in Organic Peroxide Processing
Objective
To determine appropriate vent sizing for emergency pressure relief in the processing of organic peroxides, specifically dicumyl peroxide (DCP), using Phi-TEC II adiabatic calorimetry. The study aims to provide accurate thermal data to design effective relief systems and prevent catastrophic failures.
Requirements
- Identify critical thermal parameters, including onset temperature, maximum self-heating rate, and pressure rise.
- Assess the impact of initial back pressure and fill level on gas generation.
- Scale up experimental findings to design an effective emergency relief system.
- Ensure compliance with safety standards and best practices for process safety management.
Solution
To address these requirements, a series of low thermal inertia experiments were conducted using Phi-TEC II. The approach included:
- Kinetics Analysis: Examined the rate of decomposition and self-heating behavior to determine reaction speed and predict escalation scenarios.
- Thermodynamic Characterization: Measured adiabatic temperature rise and energy release to quantify the thermal hazard and energy balance in runaway conditions.
- Fluid Dynamics Evaluation: Assessed gas generation and pressure buildup dynamics to ensure appropriate vent design for handling multiphase flows.
- These experiments allowed the simulation of worst-case industrial scenarios and provided high-fidelity data for relief system design.
Results
- Integrated Hazard Understanding: Faster decomposition reactions combined with high thermal energy release and variable gas generation rates necessitate vent designs that accommodate rapid pressure escalation and multiphase flow conditions.
- Influence of Initial Pressure and Fill Level: Higher back pressure significantly increased maximum temperature and pressure rise rates, while gas generation was up to 2.3 times higher in open-cell experiments than in closed systems.
- Vent Sizing Considerations: Traditional models underestimated gas generation and pressure rise, emphasizing the necessity of accounting for non-equilibrium gas expansion in vent design.
- Process Safety Enhancement: Incorporating Phi-TEC II data led to more accurate vent sizing, reducing the risk of under-designed relief systems and improving overall safety strategies.
Conclusion
This case study emphasizes that an accurate approach to vent sizing must integrate kinetics, thermodynamics, and fluid dynamics to ensure comprehensive safety assessments. By leveraging Phi-TEC II adiabatic calorimetry, industrial facilities can design effective emergency relief systems, ensuring safe and efficient operation. This approach enhances process safety and risk management strategies, preventing potential accidents and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Comprehensive Process Safety Solutions
H.E.L delivers process safety solutions across the full development lifecycle, helping you identify and mitigate hazards.
About H.E.L Group
For over 30 years, H.E.L Group has been at the forefront of innovative scientific instrumentation for battery testing and safety analysis, serving researchers and manufacturers worldwide.
Our team of engineers and scientists combines deep expertise in electrochemistry, thermal analysis, and precision measurement to develop instruments that set the standard for battery testing excellence.
- ISO 9001 Certified
- Global Support Network
- 30+ Years Experience
- Continuous Innovation